
Photo by Boitumelo Phetla on Unsplash
Dapps in Action: Real-World Examples of Decentralized Applications in Different Industries
What a Dapp is and How it differs from a Traditional Application.
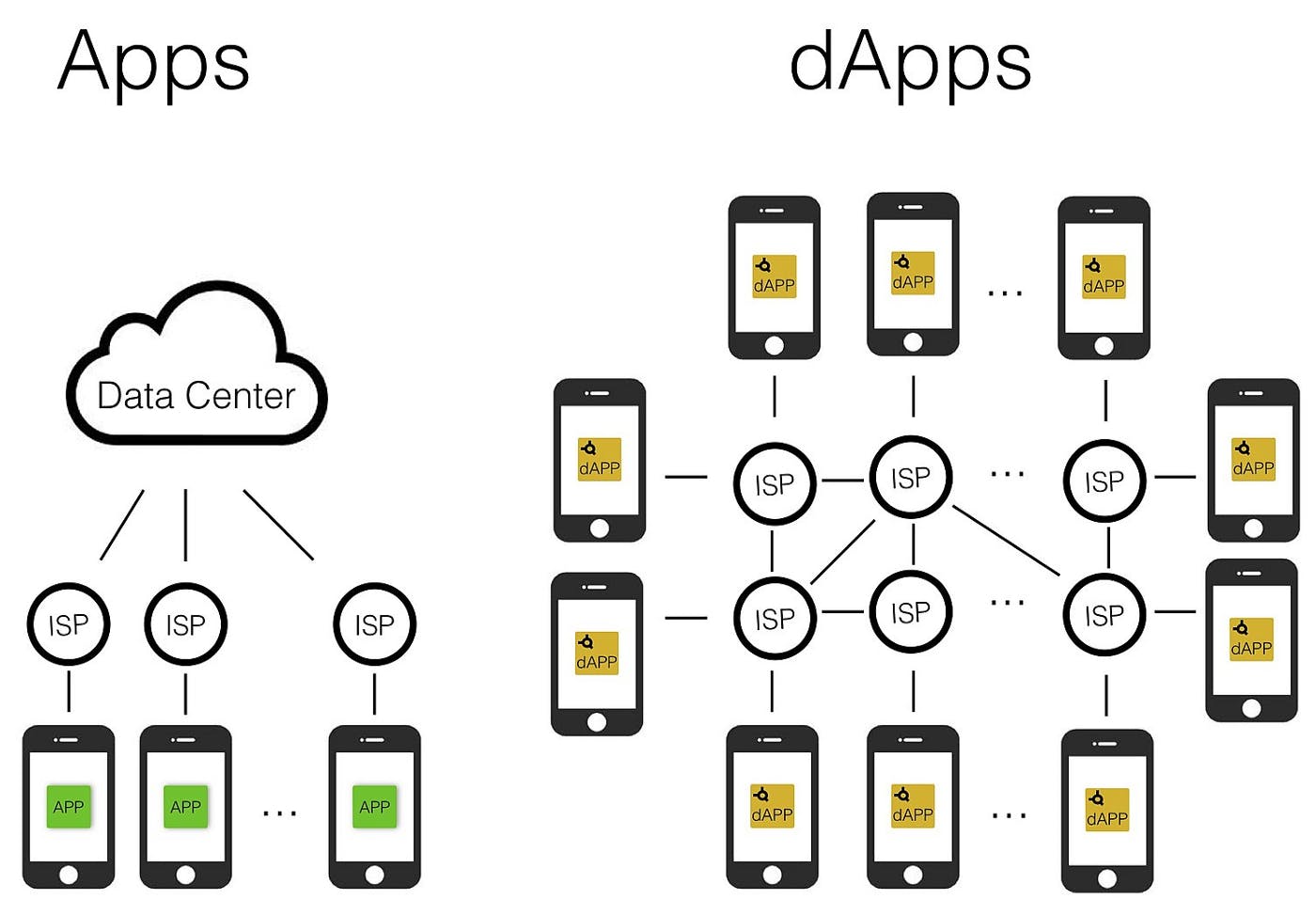
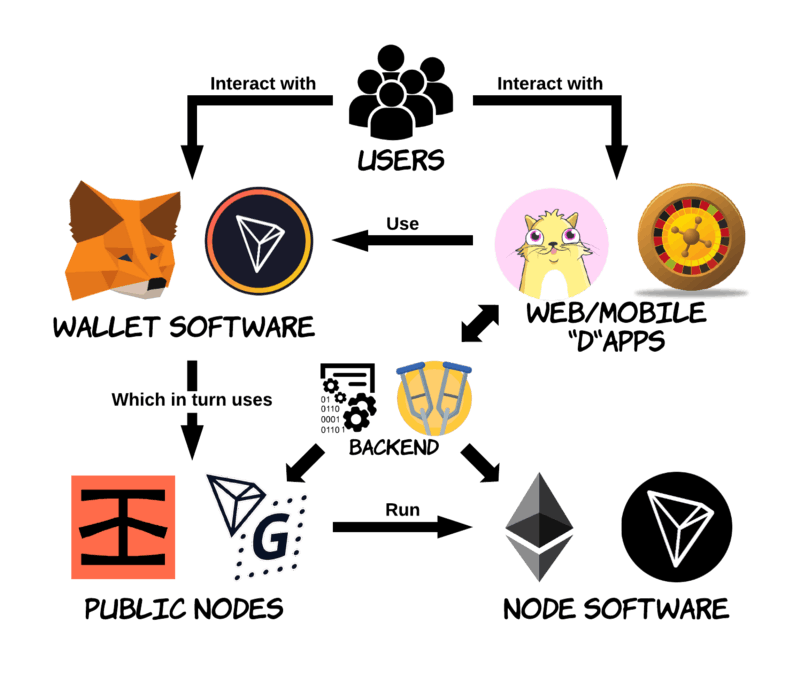
Dapp (Decentralized Application) is a software application that runs on a decentralized platform, such as Ethereum. It uses blockchain technology to enable secure and transparent record-keeping and execution of code.
Unlike traditional applications, which are typically centralized and controlled by a single entity or organization, Dapps are decentralized and rely on a network of computers (also known as nodes) to validate and execute transactions. This makes Dapps resistant to censorship and tampering, as any changes to the code or data stored on the blockchain must be agreed upon by a majority of the nodes in the network.
Dapps can be used for a variety of purposes, including financial transactions, social networking, governance, and more. They are often open source and may have their own native tokens or cryptocurrencies that are used to facilitate transactions within the Dapp.
Benefits of using a Dapp
There are several benefits to using a Dapp:
Decentralization: Dapps are decentralized, meaning that they are not controlled by any single entity or organization. This makes them resistant to censorship and tampering, as any changes to the code or data stored on the blockchain must be agreed upon by a majority of the nodes in the network.
Security: Dapps use blockchain technology, which is known for its security and reliability. Transactions on a blockchain are cryptographically signed and stored in a decentralized manner, making it difficult for them to be altered or tampered with.
Transparency: Dapps are transparent, as all transactions and code execution are recorded on the blockchain and can be viewed by anyone. This helps to build trust and ensures that the Dapp is functioning as intended.
Peer-to-peer interactions: Dapps enable peer-to-peer interactions, allowing users to interact directly with one another without the need for intermediaries. This can lead to faster, cheaper, and more efficient transactions.
New forms of economic activity: Dapps have the potential to enable new forms of economic activity and disrupt traditional business models. For example, a Dapp could be used to facilitate peer-to-peer lending or to create a decentralized marketplace for buying and selling goods and services.
Open source: Many Dapps are open source, meaning that anyone can review and contribute to the code. This can lead to a stronger and more transparent development process.
Examples of Dapps in Different Industries
There are several types of Dapps, classified based on their function and the consensus mechanism they use.
Finance: Cryptocurrency exchanges, such as Coinbase and Binance, are Dapps that enable users to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies. Decentralized finance (DeFi) Dapps, such as Compound and MakerDAO, allow users to lend, borrow, and trade cryptocurrencies using smart contracts.
Social networking: Steemit is a Dapp that allows users to create and curate content, earn rewards in the form of the STEEM cryptocurrency, and vote on content created by others.
Governance: Aragon is a Dapp that allows users to create and manage decentralized organizations (DAOs) using smart contracts. DAOs can be used for a variety of purposes, such as managing projects, creating voting systems, and more.
Supply chain management: VeChain is a Dapp that enables users to track the movement of goods and verify their authenticity using blockchain technology.
Online marketplaces: OpenBazzar is a Dapp that allows users to buy and sell goods and services using cryptocurrency.
Gaming: Axie Infinity is a Dapp that allows users to collect, breed, and trade digital creatures (called Axies) using the Ethereum blockchain.
Identity verification: Civic is a Dapp that allows users to securely store and manage their identity information, such as their name and address, on the blockchain.
Challenges faced by Dapps
Scalability: One of the main challenges faced by Dapps is scalability. Blockchain networks can only process a limited number of transactions per second, which can limit the number of users that a Dapp can support. This is a particularly significant challenge for Dapps that are intended for widespread use, such as cryptocurrency exchanges.
User adoption: Another challenge faced by Dapps is user adoption. Many people are still unfamiliar with blockchain technology and may be hesitant to use a Dapp, especially if it requires them to hold and use a cryptocurrency.
Complexity: Dapps can be complex and may require users to have some technical knowledge in order to use them. This can be a barrier to entry for some users.
Integration with existing systems: Dapps may also face challenges in integrating with existing systems and processes, as they operate on a decentralized platform that is separate from traditional systems.
Regulation: Dapps may also face regulatory challenges, as the regulatory environment for blockchain and cryptocurrency is still evolving in many jurisdictions.
Summarizing the key points
A Dapp is a decentralized application that runs on a decentralized platform, such as Ethereum, and uses blockchain technology to enable secure and transparent record-keeping and execution of code.
Dapps are decentralized, meaning that they are not controlled by any single entity or organization. This makes them resistant to censorship and tampering.
Dapps rely on a network of computers (nodes) to validate and execute transactions.
Dapps have the potential to enable new forms of economic activity and disrupt traditional business models.
Dapps can be used for a variety of purposes, including financial transactions, social networking, governance, and more.
Dapps are often open source and may have their own native tokens or cryptocurrencies that are used to facilitate transactions within the Dapp.
Examples of Dapps include cryptocurrency exchanges, prediction markets, and online marketplaces.
Dapps face challenges, such as scalability and user adoption, but the Dapp community and the platforms on which Dapps run are working to address these issues.
The future potential of Dapps is vast and will likely depend on the continued development of the underlying blockchain technology and the adoption of Dapps by users.
