Table of contents
What is SegWit?
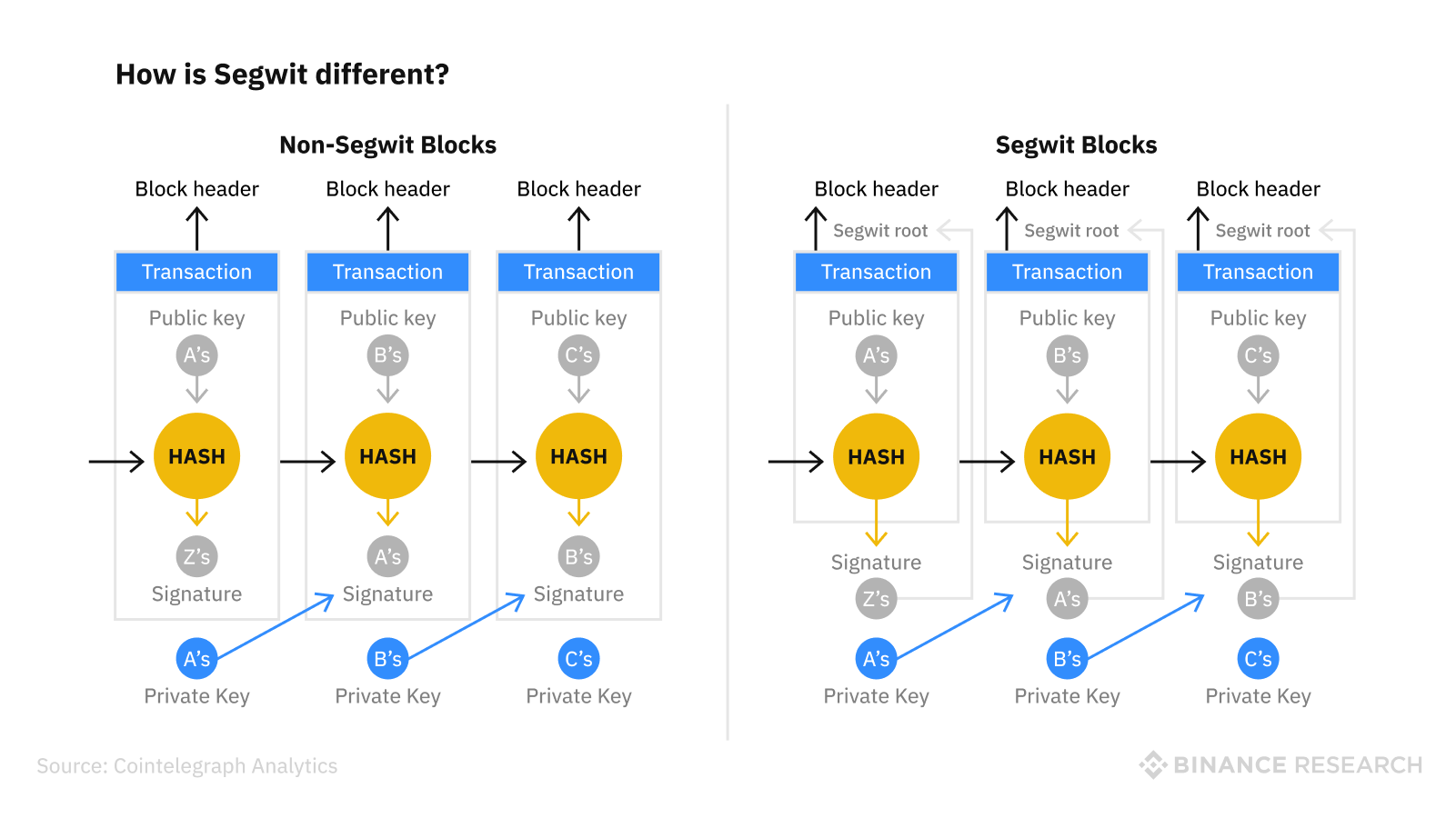
Segregated Witness (SegWit) is a proposal for a soft fork in the Bitcoin protocol that was implemented to address several issues with the cryptocurrency. SegWit separates the transaction data from the witness data in a Bitcoin transaction, freeing up space in the blocks on the blockchain and allowing for more transactions to be included in each block. This can help improve the scalability and efficiency of the Bitcoin network. In addition, SegWit addresses the issue of transaction malleability, which occurs when the data within a transaction can be modified before it is included in a block. This can cause issues with the transaction being confirmed or processed correctly. SegWit's separation of the transaction data and the witness data helps to prevent transaction malleability. Overall, SegWit is an important upgrade to the Bitcoin protocol that has helped improve the security and scalability of the network.
Why SegWit is Important?
Improved scalability: SegWit frees up space in the blocks on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Enhanced security: SegWit helps to prevent transaction malleability.
Lower transaction fees: By increasing the block size limit and allowing for more transactions to be processed on the network, SegWit can help to reduce transaction fees. This can make Bitcoin more accessible and appealing to users, particularly those who are making small transactions.
Increased adoption: SegWit has been widely adopted by the Bitcoin community and has played a key role in the development of the cryptocurrency. Its implementation has helped to build confidence in the security and scalability of the network, which may encourage more people to use Bitcoin.
Overall, SegWit is an important upgrade to the Bitcoin protocol that has helped to improve the security, scalability, and adoption of the cryptocurrency.
How SegWit Work?
Here's an example of how SegWit works:
Alice wants to send 1 BTC to Bob. She creates a transaction that includes the inputs (the previous transactions that are being spent), the outputs (the new transactions being created), and the witness data (the cryptographic signatures that prove ownership of the funds being spent). Before SegWit, the transaction data and the witness data would be included in the same block on the Bitcoin blockchain. With SegWit, the transaction data and the witness data are separated and the witness data is stored outside of the main block data. This frees up space in the block and allows for more transactions to be included. The transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network and is added to a block by a miner. Bob can now use the 1 BTC that he received from Alice.
